Why We Love It
-
$77,190Potential Avg. Salary
-
-0.5%Job Growth Rate
-
Growing IndustryCareer Attribute
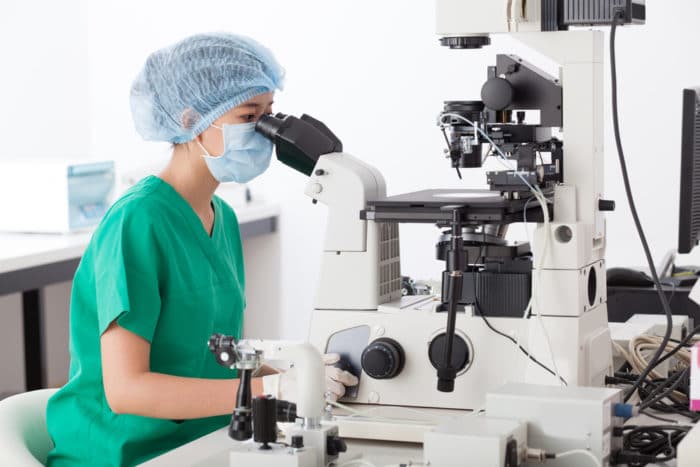
Embryologists are scientists and medical professionals that focus on fertility treatments and reproductive research. They assist with fertilization when patients are having trouble conceiving by running fertility tests, harvesting eggs and sperm, and conducting in vitro fertilization procedures.
Recommended Schools
What is an Embryologist?
The following job responsibilities are common for individuals in embryologist roles:
- Meet with patients who are struggling to conceive to discuss possible treatment options
- Conduct fertility testing on patients to determine the cause of conception problems
- Harvest sperm and eggs to be used in in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedures
- Monitor inseminated eggs for signs of fertilization
- Ensure that eggs, sperm, and embryos are properly stored and cared for in laboratories
A Day in the Life
Embryologists are scientists and medical professionals who specialize in fertility and help couples overcome fertility problems. When an individual or couple is struggling to conceive, they visit an embryologist who provides counseling, advice, and potential treatment options. Initially, the embryologist may recommend simple treatments to encourage conception. For example, the embryologist may recommend monitoring cycles to determine periods of fertility.
If simple solutions do not result in conception, the embryologist may conduct fertility testing to determine the source of the problem. The results of the fertility test may point to fertility problems for one or both of the parents. With the results of the fertility test, the embryologist can recommend more aggressive treatments, such as fertility drugs, artificial inseminations, or in vitro fertilization (IVF). Embryologists teach patients how and when to administer fertility drugs when needed, and they may conduct artificial insemination procedures.
When patients choose to pursue IVF, the embryologist is responsible for harvesting both the sperm and the egg. The egg and sperm are then combined in a laboratory dish and monitored for fertilization. If fertilization occurs, it results in an embryo. The embryo can then be transferred to the mother’s uterus, resulting in pregnancy. The process of IVF requires detailed work and special care to ensure that harvested eggs and sperm and manually created embryos are properly stored and handled in labs.
Typical Work Schedule
Embryologists typically work full-time schedules but commonly work irregular hours. Because an embryologist must always be available in a lab to monitor embryo development, they commonly work evening and weekend shifts. However, they may alternate weekend shifts with other embryologists in a practice, so weekend work may only be required on occasion.
Projected Job Growth
Because of advances in the field of embryology, modern embryologists can more effectively overcome fertility issues for their clients. This should result in an increased demand for embryologists in the coming decade due to an increased number of successes in the field.
Typical Employers
Most embryologists work for private practices or fertility clinics. They may also work in research and development, for colleges/universities, or they may be self-employed and operate their own practices.
Recommended Schools
How To Become an Embryologist
The first step in the path to becoming an embryologist is to earn a bachelor’s degree. Aspiring embryologists commonly major in subjects like biology, medical laboratory science, or a related field. While a bachelor’s degree will allow you to find entry-level work in medical laboratories and begin accruing professional laboratory experience, it is not sufficient for practicing embryology. To conduct embryology procedures in laboratories, you’ll need to earn a relevant master’s degree.
With a master’s degree, you’ll be able to find work in labs conducting and observing IVF procedures. However, you will not be qualified to work with patients or conduct independent research. To take on the responsibilities of these two roles, you’ll need to earn either a medical degree (M.D.) or a Ph.D. With a Ph.D., you’ll be qualified to conduct independent research in the field of embryology and will be able to experiment in the field to uncover new treatments or procedures for overcoming infertility.
To treat patients or prescribe medicines, a medical degree is required. Students can enter medical school directly after earning a bachelor’s degree, so a master’s degree may not be required for this career path. With a medical degree, you can qualify for licensure to practice as a medical professional in your state. However, embryology is not a common focus offered by medical schools, so many embryologists pursue both a medical degree and Ph.D. The medical degree qualifies them to treat patients, and the Ph.D. qualifies them to conduct research and focus their studies on embryology.
Embryologist Salary Data
We’ve provided you the following to learn more about this career. The salary and growth data on this page comes from recently published Bureau of Labor Statistics data while the recommendations and editorial content are based on our research.
National Anual Salary
Low Range
$57,160Average
$77,190High Range
$112,820National Hourly Wage
Low Range
$27/hrAverage
$37/hrHigh Range
$54/hrHow do Embryologist salaries stack up to other jobs across the country? Based on the latest jobs data nationwide, Embryologist's can make an average annual salary of $77,190, or $37 per hour. On the lower end, they can make $57,160 or $27 per hour, perhaps when just starting out or based on the state you live in.
Salary Rankings And Facts
#156 Nationally for All Careers
Above Average Salary Nationally
Highest Education Among Embryologists
- 19.6% Doctorate
- 32% Masters
- 43.8% Bachelors
- 2.2% Associates
- 2.1% College
- 0.2% High School
- 0.1% Less than High School
Job Growth Projections and Forecast
2014 Total Jobs
36,4002024 Est. Jobs
36,200Job Growth Rate
-0.5%Est. New Jobs
-200How does Embryologist job growth stack up to other jobs across the country? By 2024, there will be a change of -200 jobs for a total of 36,200 people employed in the career nationwide. This is a -0.5% change in growth over the next ten years, giving the career a growth rate nationwide of Above Average.
Growth Rankings And Facts
#626 Nationally for All Careers
Above Avg. Growth Nationally
What Companies Employ The Most Embryologists
| Industry | Current Jobs | New Jobs Needed | % Increase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Federal government, excluding postal service | 17,600 | -1,700 | -2% |
| Research and development in the physical, engineering, and life sciences | 5,800 | 400 | 0% |
| Colleges, universities, and professional schools; state | 5,300 | 200 | 0% |