If you have been wanting to enter the healthcare industry, you might be confused between a medical assistant or a physician assistant. Even though these careers sound similar, there are many differences between the two.
So what is a medical assistant?
Medical assistants are healthcare workers that provide support services to nurses, physicians, and other healthcare professionals. Their duties generally include clinical and administrative tasks, from scheduling appointments to assisting physicians with bedside procedures.
Also see: 12 Reasons to Become a Medical Assistant
A physician assistant is a medical provider who can generally also treat and diagnose illnesses. Their general duties also include assisting with surgeries and other types of critical care. Physician assistants are sometimes also allowed to prescribe medications without the supervision of a physician.
Read on to learn more about the similarities and differences between medical and physician assistants, how much they earn, and more so that you can decide which one suits you best.
Read: National Certified Medical Assistant NCMA
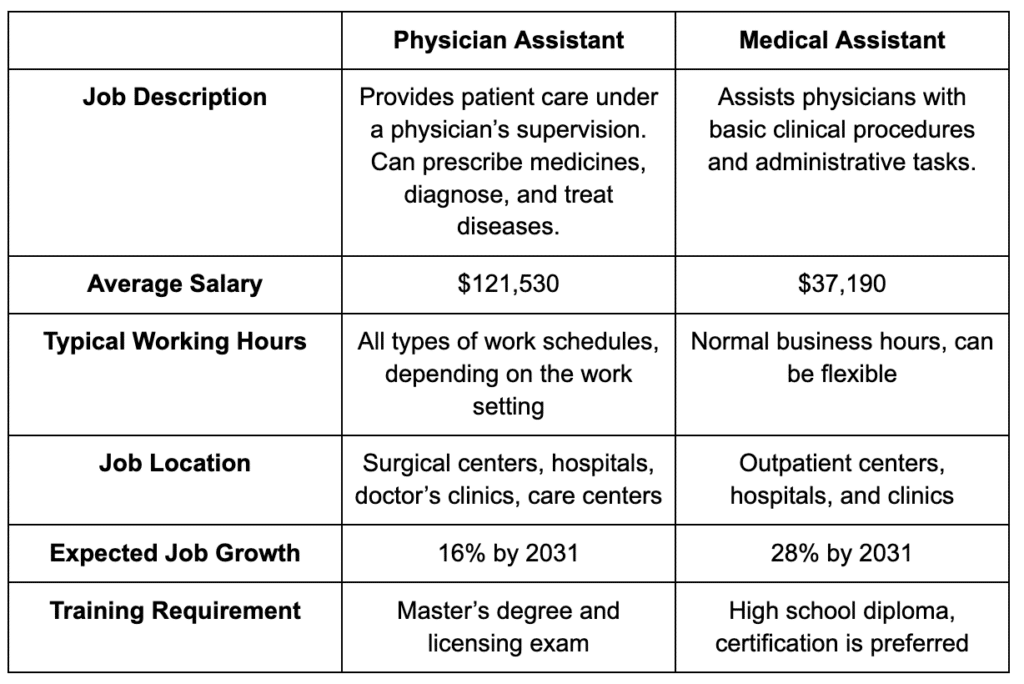
Medical Assistants vs Physician Assistants: Overview
While medical assistants provide support with basic and routine clinical and administrative tasks, such as taking vital signs, recording medical histories, and scheduling appointments, physician assistants are advanced healthcare professionals who diagnose and treat illnesses, prescribe medications and even perform some medical procedures.
Physician assistants require a master’s degree from an accredited program and must pass a certification exam to practice.
They work in close proximity to physicians and have a broad scope of practice that allows them to work in a variety of healthcare settings, including primary care, emergency medicine, and surgery.
Let us see how the two professions compare:
Medical Assistant: Overview
Medical assistants work in various healthcare settings, including doctors’ offices, clinics, hospitals, and outpatient care centers. In addition to clinical and administrative tasks, they may assist with medical procedures, collect and prepare laboratory specimens, and provide patient education.
Medical assistants generally work 40 hours per week, and their schedules may include day and evening shifts.
The general medical assistant job duties include:
- organizing the office
- preparing rooms for patients
- taking vital signs
- assisting with basic medical procedures
- coordinate with insurance companies
- scheduling appointments
- send billing reminders
- draw blood
- collect urine samples
- help with simple wound dressings
- A high school diploma or GED is typically required to qualify as a medical assistant. While having a certification or degree is not mandatory, it is recommended.
Read: Can Medical Assistants Draw Blood?
One can become a certified medical assistant by taking an online certification course, enrolling in an in-person certification program, or completing an associate degree program. Following the completion of the selected course, you would need to pass a certification exam.
Also see: Is Medical Assistant Degree Required?
Also read: Where Can Medical Assistants Work?
Physician Assistant: Overview
There is a similarity between a physician assistant and a physician in many aspects. They provide medical care to patients across various healthcare settings, ranging from family practice clinics to specialized cardiac surgery centers.
Physician assistants have the authority to diagnose illnesses, recommend treatments, and prescribe medications. They can consult with physicians when they need guidance or in situations that require a higher level of complexity.
Medical assistants can assist physician assistants in the same way they help doctors. The general duties of a physician assistant include:
- diagnosing illnesses
- prescribing medications
- assisting in surgeries
- placing stitches
- ordering lab and diagnostic tests
- interpreting the results of these tests
- educating patients on their conditions
To become a physician assistant, you will need to first obtain a bachelor’s degree and then complete a master’s degree from an accredited program.
See also: Medical Assistant Degree vs Certificate
After completing the program, you are required to pass a licensure exam before practicing. The entire process typically takes about six years.
Physician assistants typically work in hospitals and private practice offices. They usually work during daytime hours but may be required to be on-call for nights and weekends.
Also see: Medical Assistant Programs Cost
Major Similarities Between Physician and Medical Assistants
Although they are different professions, medical and physician assistants share some similarities in their roles and responsibilities within the healthcare industry.
Let us take a look at some of the key similarities between these two careers:
- Both professions are responsible for caring for patients, paying attention to their physical and emotional needs, and staying calm during emergencies.
- Additionally, medical and physician assistants need to have a solid understanding of disease control and prevention as they work with potentially sick and infectious patients.
- Lastly, both professions work under the supervision of a physician, although physician assistants typically have a larger scope of practice and can work more independently than medical assistants.
Read more on: Medical Assistant vs Dental Assistant
Major Differences Between Medical and Physician Assistants
Even though there are some similarities between the two professions, some striking differences set them apart. Some of such differences include:
- Physician assistants typically earn a much higher salary than medical assistants
- PAs must have a master’s degree and pass a licensing exam before starting their careers.
- Additionally, physician assistants have a broader scope of practice. They can perform invasive procedures, interpret lab results, and prescribe medications, while medical assistants are limited to non-invasive tasks and recording patient data.
Also read: Is Medical Assistant a Good Career?
Medical Assistant vs Physician Assistant: Job Growth and Salary Comparison
Both medical assistants and physician assistants have good job prospects with high projected growth rates.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, medical assistant jobs are projected to grow 16% from 2020 to 2030, which is much faster than the average for all occupations.
On the other hand, physician assistant jobs are projected to grow 31% from 2020 to 2030, which is also much faster than the average for all occupations.
Additionally, as you mentioned, there is a significant difference in salary between the two occupations, with physician assistants earning much more on average.
While medical assistants can choose to continue their education to become physician assistants or pursue other healthcare roles, the educational requirements to become a physician or educator are much more extensive.
Physician assistants who wish to become physicians would typically need to complete medical school, which usually takes four years, as well as residency training, which can last anywhere from three to seven years or more, depending on the specialty.
Also read: Is Medical Assistant School Hard?
Educational & Certification Requirements: Physician and Medical Assistants
Generally, medical assistants are not required to have any formal education beyond a high school diploma or equivalent. However, completing a medical assistant program from an accredited institution, which typically takes one to two years, can be beneficial in terms of job prospects and salary.
Additionally, becoming certified through a professional organization like the National Healthcare Association (NHA) can further increase job opportunities and earning potential. Certified medical assistants’ salaries are also much higher than non-certified medical assistants.
It’s worth noting that while some medical assistants may choose to become physician assistants, it’s usually more complex than becoming a medical assistant.
Also see: Medical Assistant Educational Requirements
Becoming a physician assistant requires completing a specific program designed for PAs and obtaining a master’s degree in that field, in addition to passing a licensure exam.
While a bachelor’s degree can be helpful in gaining admission to a PA program, it’s not always a requirement. Additionally, work experience as a medical assistant can be beneficial in preparing for the rigorous PA program. Still, it’s not a direct substitute for the education and training required to become a PA.
Also read: Certified Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA)

Do You Want To Become a Medical Assistant? Check Out Free Medical Assistant Masterclass!
In our masterclass you learn:
- How to be a medical assistant faster…in just 4 months!
- Avoid student debt & driving to classes
- #1 thing employers want from Medical Assistants
- How to stand-apart & get a university certificate for a strong resume
Day in the Life (Physician Assistant vs Medical Assistant)
Medical and physician assistants work to care for patients, although their roles and responsibilities differ.
For medical assistants, the day typically starts around 7 or 8 am by checking the day’s schedule and sending patient reminders. Medical assistants alternate between clinical and administrative tasks throughout the day to assist physicians and ensure smooth operations.
Physician assistants have different work schedules and might start their workday in the morning or evening. They usually begin their day by reviewing patient charts and care plans for a few hours. Afterward, they spend the rest of their day evaluating patients, making diagnoses, developing care plans, and performing specific procedures.
Also read: Medical Assistant Hours
Conclusion
The differences between a medical assistant and a physician assistant are clear yet significant. A medical assistant primarily supports healthcare teams by handling administrative tasks and aiding in basic clinical procedures, while a physician assistant takes on a more advanced role, diagnosing illnesses, prescribing medications, and providing direct patient care under a doctor’s supervision.
Both roles are crucial in the healthcare landscape, with medical assistants ensuring smooth office operations and physician assistants delivering more complex medical care. Understanding these distinctions helps individuals navigate their career choices within the diverse field of healthcare, recognizing the unique contributions each role makes to patient well-being.
Related Resources:
- How To Become a Medical Assistant
- CMA vs CNA
- CMAA vs CCMA
- Medical Administrative Assistant
- Are Medical Assistant Licenses Required
- Can Medical Assistants Give Injections or Shots
- Military Medical Assistant
- Medical Assistant vs EMT
- Accelerated Medical Assistant Program
- Medical Assistant Degree Online 6 Weeks
- 4 Week Medical Assistant Program
- Cheapest Medical Assistant Program
Related Articles
-
How to Be Successful in College in 2022 – 7 Simple Tips to Succeed
-
How Do Scholarships Work? Read This First…Truth is Shocking
-
7 Best College Majors 2024: What Should I Major In?
-
How to Choose a College – 10 Things You Must Consider in 2024
-
Why Go to College? Top 13 Benefits for Adult Students in 2022
-
Top 5 Best Alternatives to Community College for 2024